For the following calculations we will only consider plates of uniform thickness and with a uniformly distributed load over the entire surface. This will help us define minimum thickness’ for components such as pressure vessels or piston housings.
Simply Supported
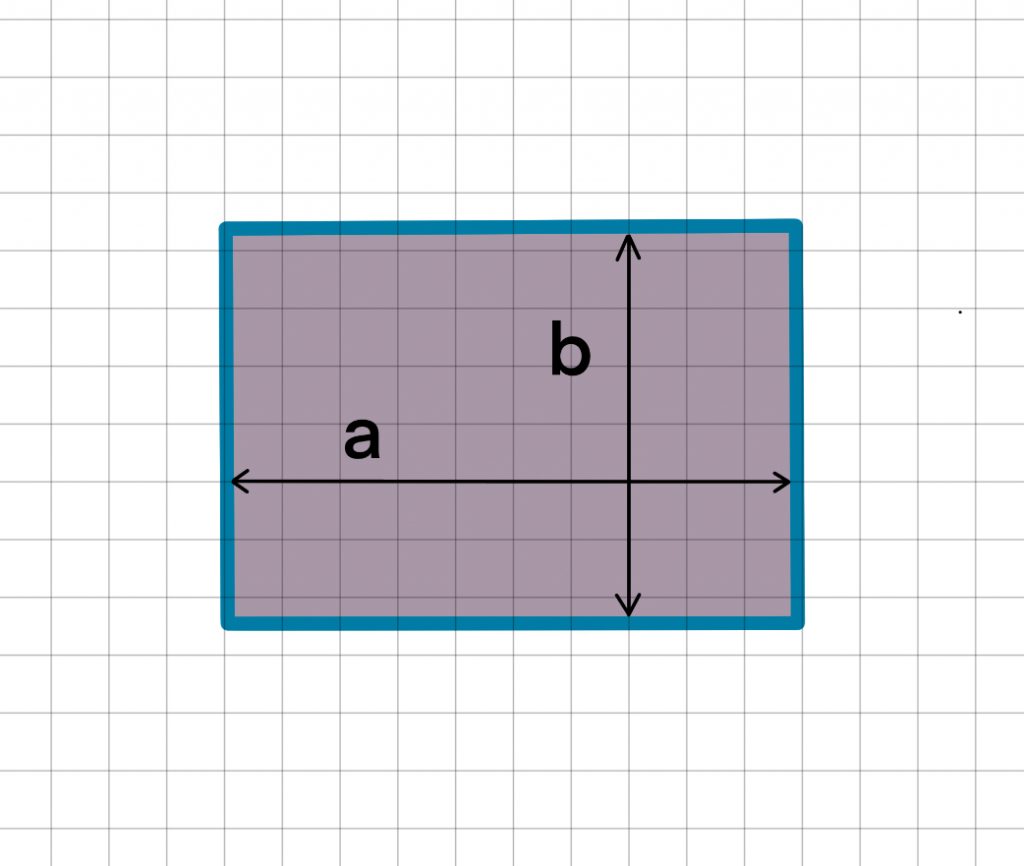
The maximum bending stress of a simply supported plate can be calculated by:
Stress at centre of plate
a=plate length, b=plate width
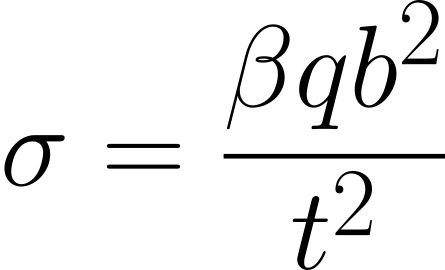
| a/b | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2874 | 0.3762 | 0.4530 | 0.5172 | 0.5688 | 0.6102 | 0.7134 | 0.7410 | 0.7476 | 0.7500 |
For values of a/b not given in table, round down to the next respective value i.e. assuming maximum stress values for conservatism.
Fixed Support
For a plate that is fixed supported i.e. built into the structure, the maximum bending stress (at the centre of longer edges) can be calculated by:
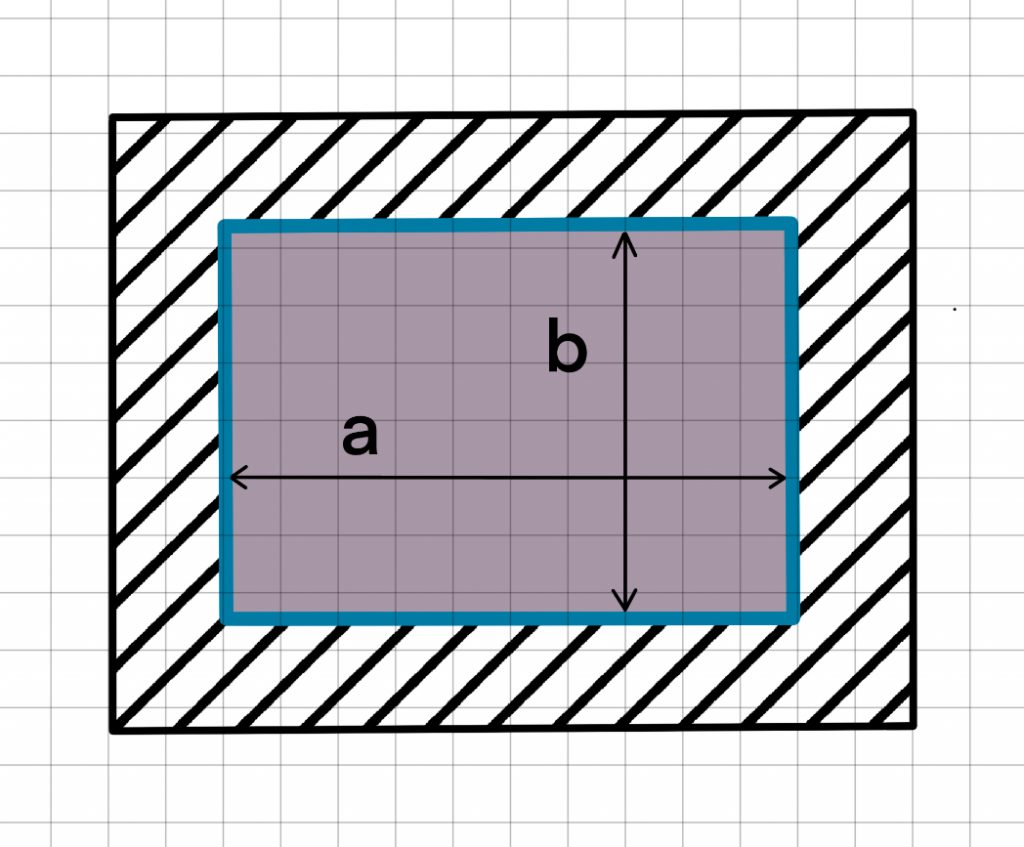
Max stress at centre of long edge
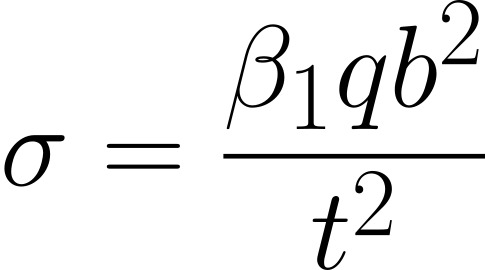
Stress at centre of plate
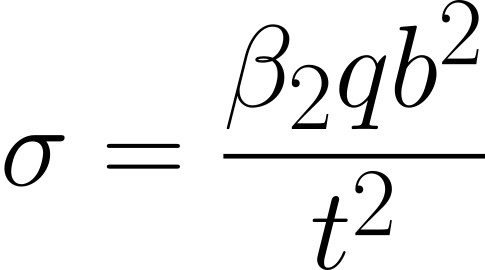
| a/b | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 2.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3078 | 0.3834 | 0.4356 | 0.4680 | 0.4872 | 0.4974 | 0.5000 | |
| 0.1386 | 0.1794 | 0.2094 | 0.2286 | 0.2406 | 0.2472 | 0.2500 |
For values of a/b not given in table, round down to the next respective value i.e. assuming maximum stress values for conservatism.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.